点击图片可以看大图
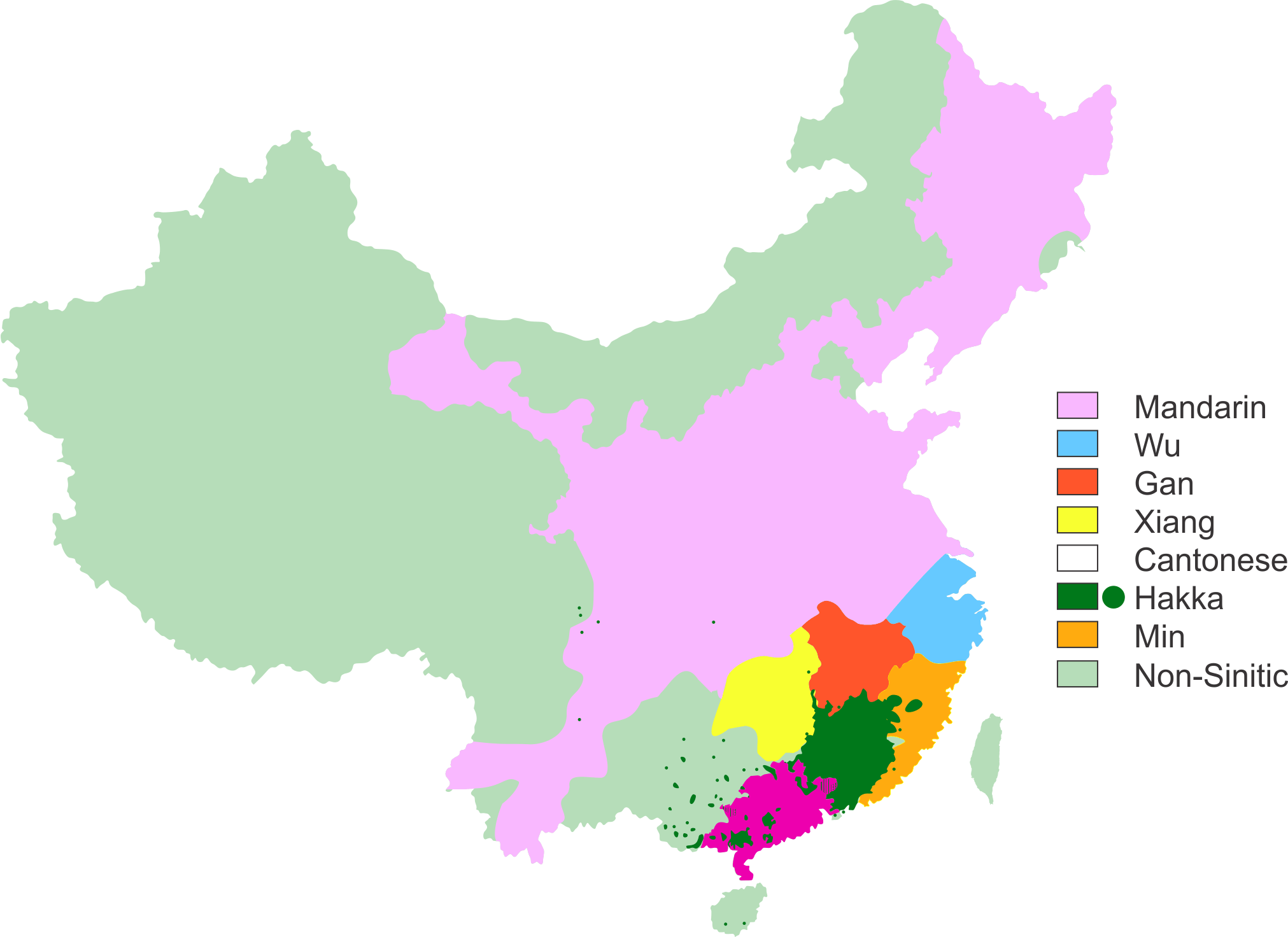
Chinese (汉语) comprises of seven main dialects, Mandarin (官话), Cantonese (广州话, 广府话), Hakka (客家话), Wu (吴语), Min (闽语), Xiang (湘语), and Gan (赣语) (Fig. 1). The variety of Mandarin based on the speech in the capital Beijing is the official national language of mainland China and is termed Pŭtōnghuà, Common language (普通话). The de facto common language in Hong Kong and overseas Chinese communities is Cantonese. Amongst the official languages of Taiwan are Mandarin, Taiwanese, and Hakka (Fig. 1).
The Chinese dialects are not mutually intelligible but are termed dialects from sociological and political points of view. Most of the dialects are themselves composed of a number of non-mutually-intelligible subvarieties. Six of the seven main dialects are in the southeast of Chinese, south of the Yangtze river. Mandarin is spoken in most of northern China and part of western China.
Han Chinese represent about 92 percent of the total Chinese population. About two-thirds of the Han population speaks a variant of Mandarin as their native tongue. A significant part of the Han population is therefore bilingual. Under these circumstances the Common language is used as a second language for formalcommunication in government, media, and education. The primary mother tongue is used for the remaining occasions such as conversation at home, between friends and relatives, entertainment, etc.
All varieties of Chinese belong to the Sino-Tibetan family of languages. Members of the Sinitic family are typically tonal, meaning that different tones, or intonations, distinguish words that otherwise are pronounced identically. Chinese by origin is monosyllabic. The vocabulary of dialects more recent in the linguistic tree such are Mandarin tend to become more polysyllabic (compound words) as an adjustment to the loss of a number of sounds compared to ancient Chinese.
Despite the diversity of speech the Han Chinese share one common script making written communication possible between people speaking mutually unintelligible dialects.
variety [və´raiəti]  n.变化;多样(性);种类 (初中英语单词)
n.变化;多样(性);种类 (初中英语单词)
spoken [´spəukən]  speak的过去分词 (初中英语单词)
speak的过去分词 (初中英语单词)
western [´westən]  a.西的;西方的 (初中英语单词)
a.西的;西方的 (初中英语单词)
therefore [´ðeəfɔ:]  ad.&conj.因此;所以 (初中英语单词)
ad.&conj.因此;所以 (初中英语单词)
formal [´fɔ:məl]  a.正式的;外表的 (初中英语单词)
a.正式的;外表的 (初中英语单词)
communication [kə,mju:ni´keiʃən]  n.通信;通讯联系 (初中英语单词)
n.通信;通讯联系 (初中英语单词)
primary [´praiməri]  a.主要的 n.居首位的 (初中英语单词)
a.主要的 n.居首位的 (初中英语单词)
entertainment [,entə´teinmənt]  n.招(款)待;联欢会 (初中英语单词)
n.招(款)待;联欢会 (初中英语单词)
distinguish [di´stiŋgwiʃ]  v.区分;识别;立功 (初中英语单词)
v.区分;识别;立功 (初中英语单词)
otherwise [´ʌðəwaiz]  ad.另外 conj.否则 (初中英语单词)
ad.另外 conj.否则 (初中英语单词)
origin [´ɔridʒin]  n.起源;由来;出身 (初中英语单词)
n.起源;由来;出身 (初中英语单词)
vocabulary [və´kæbjuləri, vəu-]  n.词汇;词汇量 (初中英语单词)
n.词汇;词汇量 (初中英语单词)
amongst [ə´mʌŋst]  prep.其中之一 =among (高中英语单词)
prep.其中之一 =among (高中英语单词)
significant [sig´nifikənt]  a.重要的;意义重大的 (高中英语单词)
a.重要的;意义重大的 (高中英语单词)
pronounced [prə´naunst]  a.发出音的;显著的 (高中英语单词)
a.发出音的;显著的 (高中英语单词)
linguistic [liŋ´gwistik]  a.语言的;语言学的 (高中英语单词)
a.语言的;语言学的 (高中英语单词)
adjustment [ə´dʒʌstmənt]  n.调整;适应;调解 (高中英语单词)
n.调整;适应;调解 (高中英语单词)
mainland [´meinlənd]  n.大陆;本土 (英语四级单词)
n.大陆;本土 (英语四级单词)
composed [kəm´pəuzd]  a.镇静自若的 (英语四级单词)
a.镇静自若的 (英语四级单词)
southeast [,sauθ´i:st]  n.&a.东南(方) (英语四级单词)
n.&a.东南(方) (英语四级单词)
yangtze [´jæŋtsi:]  n.长江 (英语四级单词)
n.长江 (英语四级单词)
overseas [,əuvə´si:z]  ad.(向)海外 a.海外的 (英语六级单词)
ad.(向)海外 a.海外的 (英语六级单词)
diversity [dai´və:siti]  n.差异;多样性 (英语六级单词)
n.差异;多样性 (英语六级单词)


 京公网安备 11011202003401号
京公网安备 11011202003401号
